-
Research Article
- Thermal Environment Analysis of a Scramjet Combustor based on pseudo-Conjugate Heat Transfer Analysis with Combustion
- Seung-Min Jeong, Kyungjae Lee, Inyoung Yang, Sanghoon Lee, Yang Ji Lee, Jae-Eun Kim, Jeong-Yeol Choi
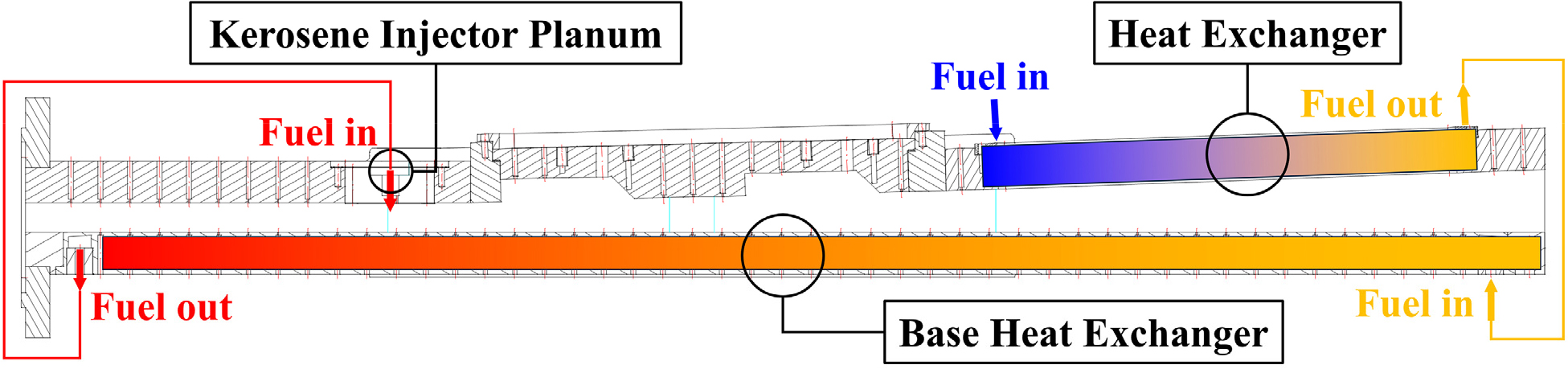
- In this study, a conjugated heat transfer (CHT) analysis was performed to investigate the thermal environment characteristics of heat exchangers and the …
- In this study, a conjugated heat transfer (CHT) analysis was performed to investigate the thermal environment characteristics of heat exchangers and the structure in a scramjet combustor. The combustor model was a kerosene-fueled tandem cavity scramjet combustor with a heat exchanger installed on both the upper and lower panels. A pseudo-CHT (p-CHT) analysis algorithm was proposed, decoupling the combustion simulation for the flow field and the heat transfer analysis for the solid structure to account for the ground combustion test time, which is on the order of tens of seconds. Combustion simulation was conducted based on the Improved Delayed Detached Eddy Simulation (IDDES) turbulence model, applying a global chemical reaction mechanism for surrogate kerosene. Wall temperature data obtained from the combustion simulation were utilized as boundary conditions for heat flux in the p-CHT analysis, and data for approximately 60 seconds were acquired. In the p-CHT analysis, the heat flux was concentrated on the rear wall region of the first cavity on the upper panel, revealing a maximum temperature distribution of approximately 1,040 K. On the lower panel, a comparatively lower heat flux was concentrated, yielding a maximum temperature peak of approximately 850 K. The temperature gradient between the upper and lower panels indicates the potential for structural stability concerns in the heat exchanger and jacket. And the location of the maximum temperature derived from the p-CHT analysis did not coincide with that from the combustion simulation. These findings suggest that the structural thermal environment is generated through the coupling of flame structure and combustor geometry conditions. Through these series of results, it was found that the proposed p-CHT analysis algorithm is capable of conducting conjugated heat transfer analysis for durations of tens of seconds with notably low computational cost. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article

- Preliminary Numerical Study on the Combustion Efficiency of a Multi-Slit Type Gas-Liquid Pintle Injector
- Subeom Heo, Youngbin Yoon, Bok Jik Lee
- The momentum ratio between oxidizer and fuel is widely known to affect the combustion efficiency of pintle injectors for liquid rocket engines. …
- The momentum ratio between oxidizer and fuel is widely known to affect the combustion efficiency of pintle injectors for liquid rocket engines. Based on TRW’s hot firing test results, many subsequent studies have set the momentum ratio to unity when designing pintle injectors to obtain maximum combustion efficiency. However, recent studies have shown that the highest combustion efficiency of gas-liquid pintle injectors was observed at momentum ratios other than 1. Therefore, this study revisits the effects of momentum ratio on the combustion efficiency of a gas-liquid pintle injector within the range of 0.3–4.4. The results show that the peak efficiency did not occur at a momentum ratio of 1, conflicting with TRW’s design recommendations. Furthermore, the effects of blockage factor and mixture ratio are also investigated. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
- Formation and Mechanical Characterization of GAP-based Polymeric Networks for Solid Rocket Propellants: A Dual Reactive Approach Using Terminal-Hydroxyl and Pendant Azide Groups
- Byoung Sun Min, Sung June Kim
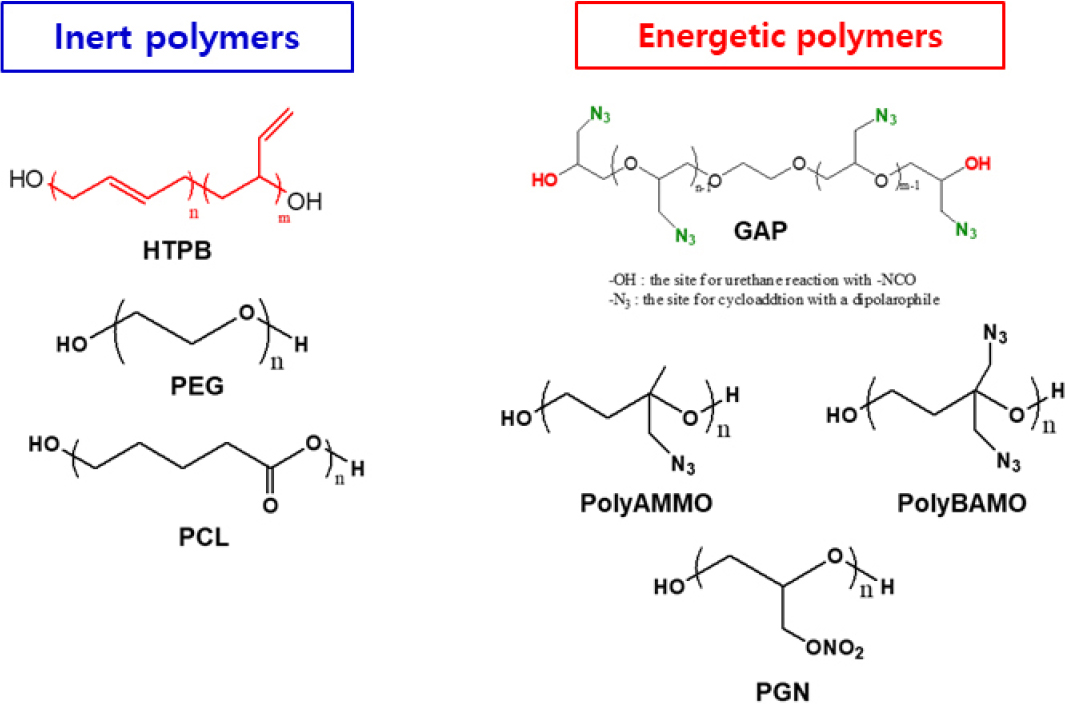
- Glycidyl azide polymer (GAP) has emerged as a promising alternative to hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene (HTPB) for use in solid propellant binders due to …
- Glycidyl azide polymer (GAP) has emerged as a promising alternative to hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene (HTPB) for use in solid propellant binders due to its inherent energetic potential and dual-reactive functionality. Featuring terminal hydroxyl and pendant azide groups, GAP enables versatile crosslinking strategies. Here, we investigated a range of curing pathways, beginning with azide-alkyne and azide-alkene cycloaddition to form triazole and triazoline-linked networks, respectively. However, limited mechanical integrity and thermal instability-particularly from triazoline structures-necessitated a hybrid curing approach. A dual-site curing strategy combining urethane linkages (via terminal hydroxyl groups) with dipolar cycloaddition (via pendant azides) produced robust three-dimensional networks. Notably, maleimide-based alkenes, despite initial foaming issues, enables stable triazoline networks when integrated within the dual-cure framework. Additionally, an asymmetric bifunctional crosslinker containing both hydroxyl and alkyne group was shown to effectively bridge both reactive sites of GAP, yielding highly elastic and resilient materials. Among the dipolarophiles evaluated, oligomeric alkynes offered the best mechanical performance, while symmetric ester-containing alkynes balanced crosslinking efficiency and energetic content. These findings highlight the tunability of GAP-based network designing and its potential for next-generation energetic binder system. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
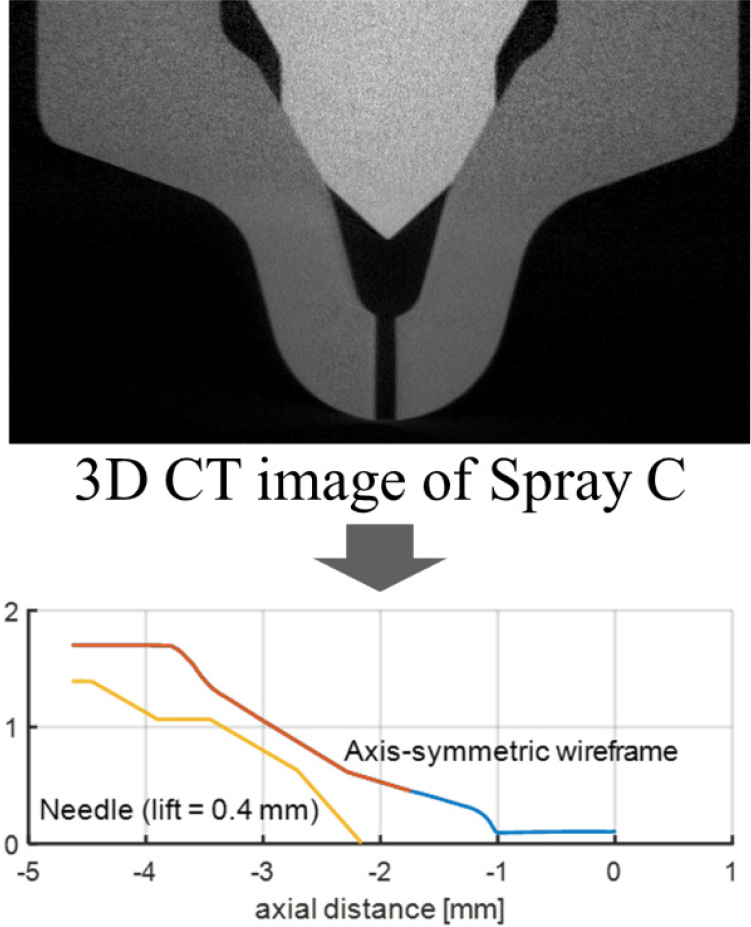
- Combined Experimental and Machine Learning Study of Injection Characteristics of High-Pressure Spray Injector
- Lin Yun, Jiho Park, Hyung Sub Sim
- This study investigates the high-pressure injection characteristics of the Engine Combustion Network (ECN) Spray C injector using a combined experimental and machine …
- This study investigates the high-pressure injection characteristics of the Engine Combustion Network (ECN) Spray C injector using a combined experimental and machine learning approach. Injection rate measurements were performed using a Zeuch-based Moehwald hydraulic discharge analyzer (HDA) under various operating conditions, including different injection pressures, chamber pressures, temperatures, and energizing durations. Building upon a previously validated artificial neural network (ANN) framework originally developed for the piezoelectric Spray A-3 injector, the same modeling strategy was applied to the solenoid-type Spray C injector to assess its cross-applicability. The ANN model, trained using Bayesian regularization backpropagation, accurately reproduced the transient and quasi-steady rate of injection (ROI) profiles of Spray C, including complex nonlinear behaviors arising from cavitation-prone nozzle geometries and short energizing durations. The model achieved a coefficient of determination (R2) exceeding 0.99, showing excellent agreement with experimental measurements. Parametric analyses revealed that injection pressure was the dominant factor influencing ROI and injected mass, whereas chamber pressure and temperature had relatively minor effects within the tested ranges. The model’s capability to capture key hydraulic and acoustic characteristics was additionally confirmed through discharge coefficient (Cd) evaluation and spectral (frequency-domain) analysis. These findings demonstrate the reliability and generalizability of the ANN-based modeling strategy for complex fuel injection phenomena, providing a computationally efficient substitute for traditional techniques and facilitating advancements in injector design and combustion system optimization. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
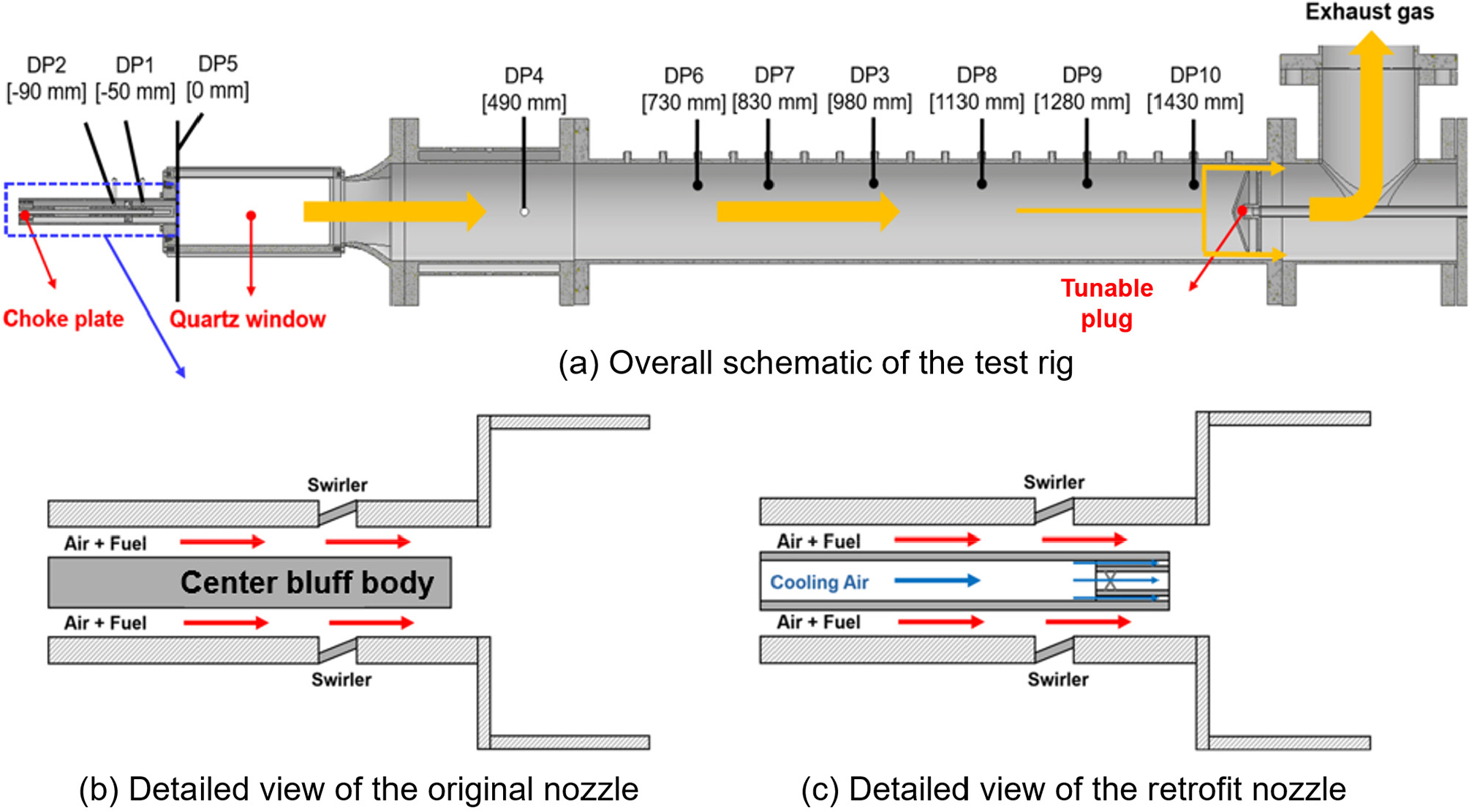
- Combustion Instability Analysis of a Gas Turbine Combustor with Varying Hydrogen Blending Ratios and Nozzle Geometry
- Jaewoo Jang, Juhwan Lee, Jaehong Choi, Youngbin Yoon, Jungmin Seok, Daesik Kim
- This study investigates the characteristics of combustion instability in a lab-scale single-nozzle combustion test rig, focusing on variations in hydrogen blending ratio …
- This study investigates the characteristics of combustion instability in a lab-scale single-nozzle combustion test rig, focusing on variations in hydrogen blending ratio and nozzle geometry. Steady-state 3D CFD simulations were performed to extract the time delay and its distribution key parameters of the flame transfer function which were then applied to a 1D network model for combustion instability analysis. The CFD results showed that changes in hydrogen blending ratio and nozzle geometry altered the flame structure, thereby affecting the time delay characteristics. These variations were found to directly influence the growth rate, helping to identify the causes of combustion instability observed in the experiments. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
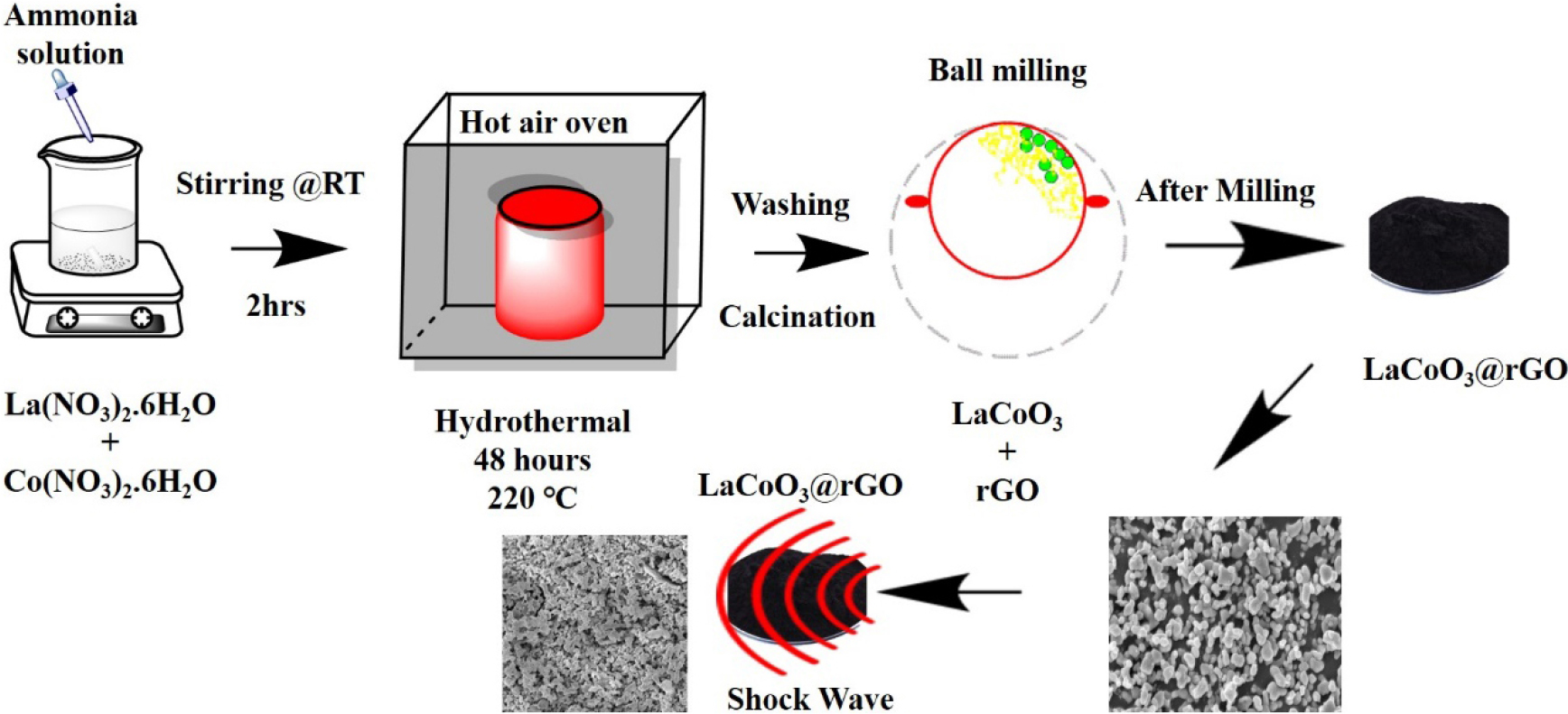
- Shock Wave-Induced Functional Properties of Lanthanum Cobalt Oxide/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites
- P. Sivaprakash, Kiwon Kim, S. A. Martin Britto Dhas, S. Esakki Muthu, Jhelai Sahadevan, Ikhyun Kim
- The current research and development sectors are concentrating their efforts on developing stable materials for extreme conditions, such as static and dynamic …
- The current research and development sectors are concentrating their efforts on developing stable materials for extreme conditions, such as static and dynamic pressure, to survive in challenging conditions. Even under extreme conditions such as high pressure and temperature, materials either retain or modify their physicochemical properties. Here, we prepared the nanocomposite of lanthanum cobalt oxide/reduced graphene oxide (LaCoO3/rGO) and investigated it under dynamic shocked conditions due to its potential method of applying pressure and temperature simultaneously. XRD confirms that the control and shocked materials are hexagonal crystal structures with space group of up R-3c H (167), and a very minor shift has been observed under shocked conditions due to the lattice expansion and it is structurally stable to the shocks. FESEM implies that the spherical particle is slightly fused to 200 shocks due to sudden pressure and temperature. Further, the LA-200 Raman spectrum shows broadened peaks with an elevated baseline, indicating strong disorder, defect formation, and possible oxygen vacancies. FTIR indicates mild shocks preserve the oxide-carbon interface, while higher shocks increase strain and contact. Furthermore, PL analysis shows that shock treatment tunes the defect chemistry and electronic interactions in LaCoO3/rGO, modulating radiative and non-radiative charge transfer depending on the shock intensity. Meanwhile, the composite materials changed from S-shaped soft ferromagnetism to paramagnetic behaviors due to shock-induced spin canting for 200 shocks. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
- Investigation of Storage Effects on the Concentration and Ignition Behavior of Hydrogen Peroxide Containing Lithium Nitrate
- Jini Yang, Minha Hwang, Jongkwang Lee
- The storage stability of hydrogen peroxide solutions with and without lithium nitrate (LiNO3) was investigated. The evaluation focused on changes …
- The storage stability of hydrogen peroxide solutions with and without lithium nitrate (LiNO3) was investigated. The evaluation focused on changes in hydrogen peroxide concentration, solution density, and ignition delay time (IDT). Samples were stored at 2°C for 100 days and analyzed before and after storage. All samples exhibited slight decreases in both concentration and density, with similar levels of degradation observed regardless of LiNO3 content. Similarly, IDTs slightly increased after storage, and the extent of increase was comparable across all samples. These results suggest that the incorporation of LiNO3 does not compromise the chemical and ignition stability of hydrogen peroxide based hypergolic propellants during storage. - COLLAPSE
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Propulsion and Energy
Journal of Propulsion and Energy
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Propulsion and Energy
Journal of Propulsion and Energy